Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon

Table of contents
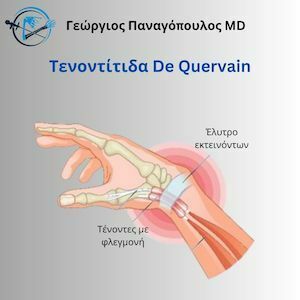
What is DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis?
DeQuervain’s was named after the Swiss surgeon who described this condition back in 1895. DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis describes the painful swelling and inflammation of the tendons of the thumb. As a result, the tendon cannot glide inside their sheath easily anymore, causing pain and difficulty in certain movements.
What causes DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis?
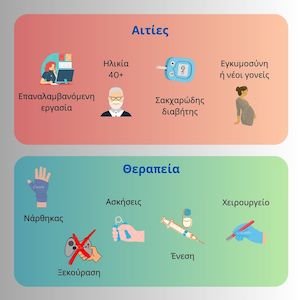
Risk factors that can precipitate DeQuervain’s include the following:
- Female sex: women are 10 times more likely to develop this condition
- Repetitive use of the thumb
- Pregnancy & lactation
- Activities that include frequent grasping, such as lifting young children, gardening, certain sports, etc.
What are the symptoms of DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis?
Symptoms usually include pain in the side of the wrist and hand, that may be precipitated by a certain activity and at times can be debilitating. Symptoms can be similar to those of thumb arthritis.
Diagnosis
History and physical exam are usually enough to confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor will typically perform the Finkelstein test. This involves making a fist with the thumb wrapped around the fingers. Moving the wrist up and down in that position typically reproduces the symptoms of DeQuervain’s.
De Quervain's may present in a similar way to thumb arthritis. Pain can be located in the same area as in a scaphoid fracture. Thus, an x-ray is useful to rule out other pathology.

Conservative treatment
The first line of treatment is commonly a trial of conservative management. This may include:
- Rest
- Activity modification
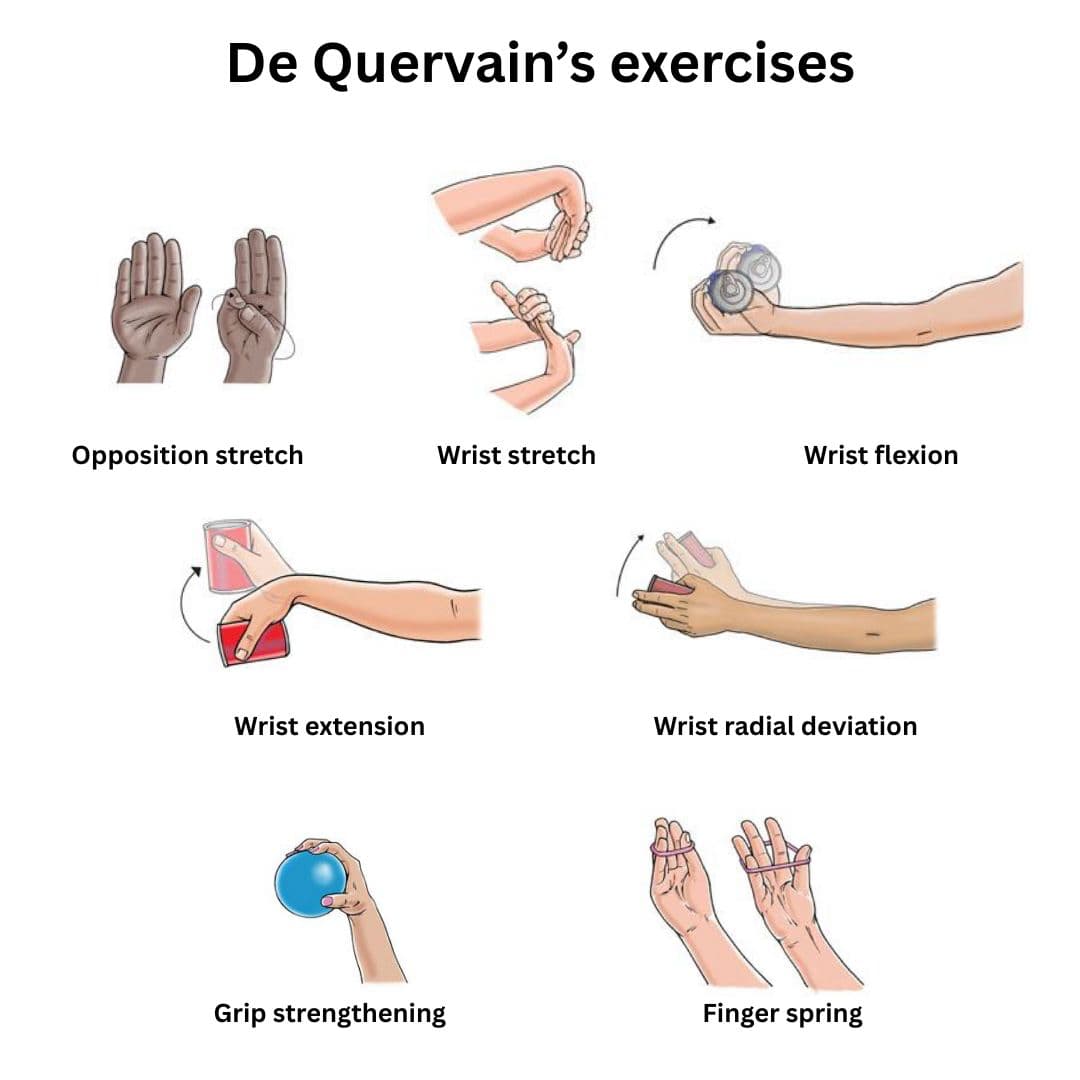
- Physiotherapy/home exercise program for strengthening and stretching exercises
- NSAIDS
- Splinting
- Steroid injection in the joint
Sometimes, De Quervain's can be related to a specific activity, ie a young parent that holds their newborn, a new mother lactating. In such cases, activity modification can be very effective.
Steroid injection can either be performed by landmarks, or US-guided. In 70% of cases, it can lead to resolution of symptoms. Cortisone may cause a flare up for the first 24-48h, before it kicks in.
Steroid injection can also have diagnostic value, in controversial cases.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails, the next option is surgery, which is performed in a day-case basis, under local anaesthetic. A small incision is made on top of the tendon and a small cut performed in the tendon sheath. This usually allows the tendon to move freely. You will have a small dressing for a few days. A hand therapy home exercise program will be given to you after the procedure.
Surgical release for De Quervain's tenosynovitis is a very successful operation, with a very low complication rate and great patient-reported outcomes.
Please contact us to schedule a consultation and discuss your options.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What Is DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis?
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is inflammation of some of the tendons of the thumb (APL, adductor policis longus & EPB, extensor policis brevis).
What causes DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis?
– Gender: male/female 1:10
– Occupational (repetitive motion)
– Pregnancy & lactation
– Activities that include frequent grasping, such as lifting young children, gardening, certain sports, etc.
How is diagnosis made?
– History & clinical exam -> Finkelstein test
– X-ray to rule out other pathology
What's the treatment?
– Rest
– Activity modification
– Hand therapy/home exercise program
– Cortisone injection
– Surgical release under local anaesthetic
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
