Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon
Το impingement syndrome ώμου ή σύνδρομο υπακρωμιακής προστριβής είναι πολύ συχνό, ειδικά σε ασθενείς >30 ετών. Συνήθως μερικές συνεδρίες φυσικοθεραπείας, μαζί με ασκήσεις στο σπίτι και ενδεχομένως μία ένεση κορτιζόνης, είναι ικανές να βελτιώσουν δραματικά τον πόνο στον ώμο και να μας επιτρέψουν μια απρόσκοπτη επιστροφή στη καθημερινότητα.
Table of contents
What is shoulder impingement syndrome?
Shoulder impingement occurs when the top edge of your shoulder blade, called the acromion, rubs against your rotator cuff beneath it, causing pain, swelling and irritation. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that originate from the shoulder blade and attach to your arm bone or humerus. The rotator cuff muscles help raise the arm overhead, as well as rotate the arm towards and away from the body. The cuff muscles sit in a small space between the acromion and the humeral head and that makes them susceptible to being pinched, leading to the so-called impingement syndrome.
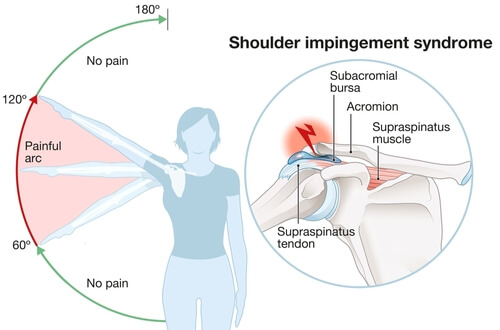
What causes impingement syndrome?
Impingement syndrome occurs when the cuff tendons rub against the acromion.
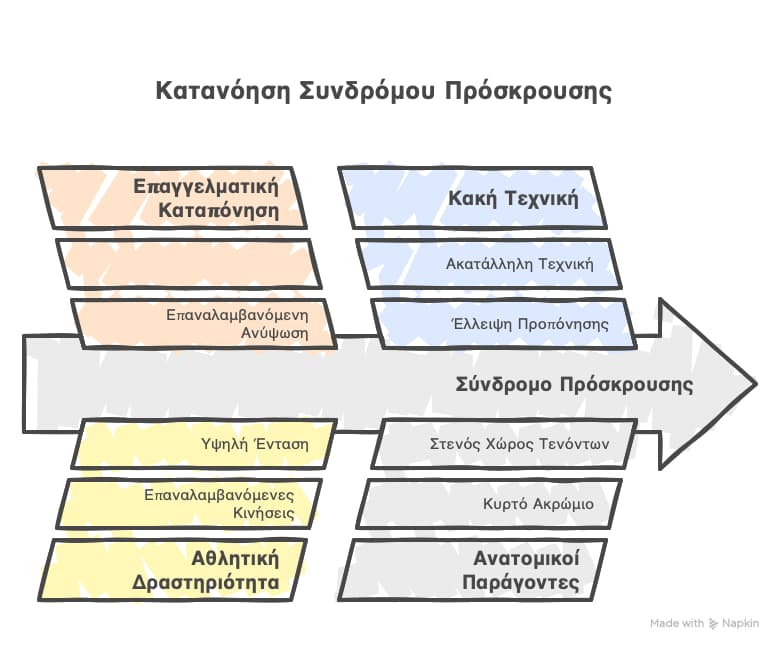
Some causes of impingement syndrome include:
- Some professions with repetitive overhead motion (painters, window cleaners)
- Sport activities with overhead repetitive rotational motion, such as swimming, baseball, volleyball and tennis
- Improper technique during sports
- Anatomic reasons. Bone spurs may develop in the acromion (might be age-related). The acromion might not be flat as usual, but curved (may run in the family).
What are the symptoms of impingement syndrome?
Symptoms usually develop gradually over weeks or months. The symptoms of impingement syndrome may include:
- Pain in the front and side of your shoulder
- Pain when lying on your arm
- Pain that worsens at night and disturbs your sleep
- Pain when lifting your arm overhead to reach something (i.e., from the cupboard)
Diagnosis
Dr Panagopoulos will take a complete history and perform a focused physical exam, including assessing your shoulder range of motion and shoulder functional tests. A painful arc between 60-120 degrees of abduction is characteristic of impingement syndrome, as well as a positive Hawkins or Neer's test. Difficulty reaching something overhead or combing one's hair are also common complaints.

An x-ray will help rule-out arthritis of the shoulder. There may also be bone spurs or a change in the outline of bone on the rotator cuff insertion (enthesitis). An MRI scan will demonstrate inflammation of the bursa or rotator cuff tears.
Conservative treatment
As with most shoulder pathology, a trial of conservative management is attempted first. Conservative management may include:
- Rest
- Activity modification
- NSAIDS
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Physical therapy/home exercise program - deltoid & cuff strengthening can definitely help to improve your pain
- Steroid injections – you may have 1 or 2 injections in the subacromial space. Success rate is about 70%. Steroid may cause some flare-up pain for 24-48 hours before kicking in. More than 2 injections may weaken the tendon and should be avoided.
Σύνδρομο πρόσκρουσης ώμου: Φυσικοθεραπεία & ασκήσεις
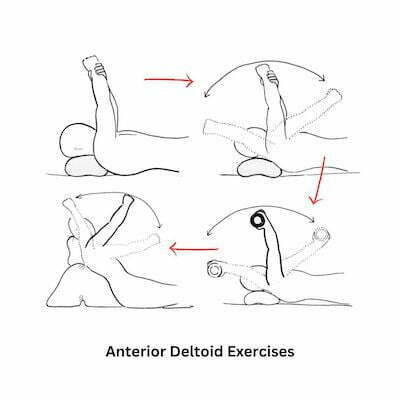
Conservative treatment is the first step for impingement syndrome. Usually some deltoid strengthening and a cortisone injection are enough to provide long-lasting relief in most patients. A few simple anterior deltoid exercises are depicted below.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails, keyhole surgery can be offered. Surgery can be performed arthroscopically. The procedure is called subacromial decompression or acromioplasty and involves shaving-contouring your acromion to increase the space available underneath for your rotator cuff.
Other shoulder problems, such as biceps tendon problems or cuff tears can be diagnosed and treated at the same time. Your arm will be placed in a sling for some time, based on the amount of arthroscopic work that was undertaken. You will start physical therapy. Recovery may take 6-8 weeks.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What is impingement syndrome?
Shoulder impingement occurs when the top edge of your shoulder blade, called the acromion, rubs against your rotator cuff beneath it, causing pain, swelling and irritation.
What does the diagnosis involve?
– History & clinical exam
– X-rays
– Ultrasound
– MRI
What's the treatment for impingement?
– Physical therapy
– Steroid injection
– Shoulder arthroscopy
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
