Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon
Distal biceps tendon rupture is the detachment of the biceps brachii tendon from its insertion on the radial tuberosity at the level of the elbow.
This injury results in loss of the normal mechanical continuity of the biceps muscle, leading to decreased elbow flexion strength and, more importantly, significant loss of forearm supination strength.
This is a common injury in men between 30-50 years of age. Treatment is usually surgical.
Key takeaways at a glance
Distal biceps tears are elbow injuries that can significantly affect strength and functionality of the upper extremity.
It typically involves middle aged men, after sudden extension or heavy lifting.
Treatment is usually surgical, especially in active and working patients.
Timely diagnosis (exam & imaging) is crucial for a favorable outcome.
Timely surgical repair within the first weeks allows more predictable recovery and restoration of strength.
Table of contents
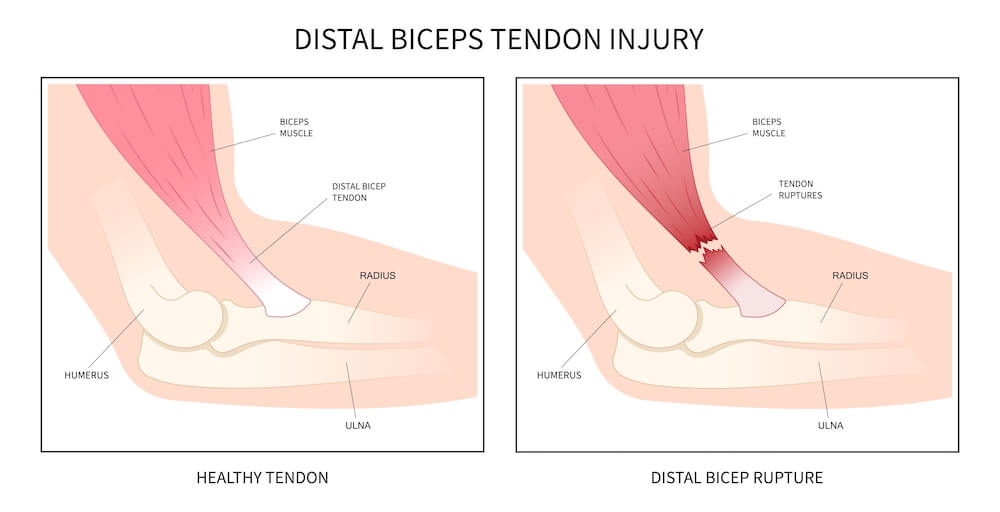
What is a distal biceps tendon rupture?
A distal biceps tendon rupture occurs when the tendon attaching the biceps muscle to the biceps tuberosity at the elbow is torn from the bone. This injury occurs mainly in men in their 30s to 50s during heavy work or lifting. Many patients will have done lots of weight training in the past or have a heavy manual job.

What causes a rupture of the distal biceps?
Distal biceps ruptures tend to occur in the dominant elbow of men (>90%) around their 40s. The mechanism of rupture usually includes excessive eccentric tension as the arm is forced from a flexed to an extended position (flexed elbow unexpectedly challenged). Risk factors include:
- Smoking (x7.5 increased risk)
- Anabolic steroids (muscle grows too quickly before tendon can catch up)
👉 A biceps rupture typically occurs after a sudden extension force is applied to the flexed elbow, as may happen while trying to catch a falling object.
What are the symptoms?
Most patients feel a sudden pop or snap at the front of their elbow with immediate pain, and subsequent bruising and swelling. This typically happens after lifting or dropping a heavy load. You may feel weakness in bending the elbow or twisting the forearm. You may also notice an altered contour of the biceps muscle – the muscle belly will sit higher up in the arm (compared to opposite uninjured side). This is called the “reverse Popeye sign.” A ruptured distal biceps tendon is usually associated with 20-30% loss of flexion strength (bending the elbow) & 40-50% loss of supination strength (rotating the forearm, as when you use a screwdriver).
- Sudden snapping sound at the time of rupture
- Swelling & bruising
- Reduced supination strength
- Reverse Popeye sign
| Symptom | Why it occurs |
|---|---|
| Loss of supination strength | Tendon does not transmit strength properly |
| Reverse Popeye sign | Muscle pulled upwards |
| Swelling / bruising | Post-injury inflammation |

In clinical practice, distal biceps tendon rupture is frequently underestimated at first, as pain may subside quickly while functional weakness becomes evident later.
How is it diagnosed?
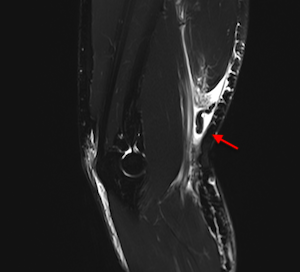
History and physical exam usually provide enough information for your doctor to make a diagnosis of a distal biceps tendon rupture. Dr Panagopoulos may order an MRI or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and assess for tendon retraction or for partial ruptures, which are also possible.
The diagnosis of distal biceps tendon rupture is based on clinical examination combined with imaging studies.
- Clinical findings may include deformity, bruising, and a positive Hook test.
- Ultrasound offers rapid and reliable confirmation in experienced hands.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful to differentiate partial from complete ruptures and to guide surgical planning.
Conservative treatment
It is not mandatory for every ruptured tendon to be repaired. You can live with your ruptured distal biceps tendon. You should expect 20-30% loss of flexion strength (bending the elbow) & 40-50% loss of supination strength (rotating the forearm, as when you use a screwdriver). If you have a low-demand job and lifestyle, you may manage well without surgery. However, if you have injured your dominant arm and engage in an active lifestyle, it is likely you will do better with surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Most active working-aged patients will choose to have distal biceps repair surgery to restore function if their tendon is fully torn. Surgery to repair the tendon should be performed during the few weeks after injury. After this time, the tendon and biceps muscle begin to scar and shorten. Further delay may preclude a straightforward, primary repair. In chronic cases, a more extensile approach may be required to retrieve the retracted and scarred distal biceps tendon. Use of an allograft may also be needed.
Treatment decisions are not based on imaging findings alone, but primarily on the patient’s functional demands and the time elapsed since injury.
Dr Panagopoulos uses a small incision to allow the most anatomical repair, restoring near to normal function. A 3-cm incision is made in the elbow crease at the front of your arm. The ruptured tendon is retrieved. Sutures are then woven up and down the tendon and used to re-attach the tendon to the bone (radial tuberosity). A drill hole is made in the radial tuberosity and the biceps is then pulled through the drill hole with an adjustable button and secured in its anatomical position. The surgery generally takes about an hour. Your elbow is placed in a bandage and a sling to protect the repair. No plaster is necessary. This operation is typically performed as a day surgery and you can go home a few hours after the procedure. You can start moving your elbow the next day to prevent stiffness.
Surgical treatment takes place ideally within 2-6 weeks, as the tendon tends to scar and shorten after this time. Primary repair may become more challenging after 8-12 weeks.
Rehabilitation - Timeline
- 0–2 weeks: protection and pain control
- 2–6 weeks: gradual restoration of motion
- 8–12 weeks: strengthening phase
- 3–6 months: return to full activity, work, and sports
When surgical repair is performed in a timely manner and followed by structured rehabilitation, most patients regain near-normal strength and function.
📌 Distal biceps tear - key facts
- Condition: Distal biceps tendon rupture
- English term: Distal biceps tendon rupture or tear
- Typical population: Middle-aged men
- Common mechanism: Sudden eccentric loading of the elbow
- Preferred treatment for complete rupture: Surgical repair
- Optimal timing for surgery: Within 2–6 weeks
- Expected recovery time: Approximately 3–6 months
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What is a distal biceps tendon rupture?
A distal biceps rupture occurs when the tendon attaching the biceps muscle to the biceps tuberosity at the elbow is torn from the bone.
Who is more susceptible?
Men between the ages of 30-50.
What's the usual mechanism of injury?
Hyperextension load on a flexed elbow.
What are the symptoms?
– Elbow pain and snapping sensation at the time of the injury
– Swelling and bruising
– Reverse Popeye sign -> biceps muscle retracted superiorly
How is diagnosis made?
– History & clinical exam
– Ultrasound or MRI scan
What if I don't have surgery?
You will lose approximately 50% of supination strength and 20-30% of flexion strength.
How is surgery performed?
Surgery involves reattachment of the distal stump of the tendon to the bicipital tuberosity of the radius by means of a metallic button.
How is rehabilitation? Do I need physiotherapy?
Recovery is fast. Physiotherapy is important for regaining function & strength.
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
