Shoulder pain is a common orthopaedic complaint that affects millions of people worldwide. The shoulder is a complex joint with a wide range of motion, making it susceptible to various injuries and conditions. In this blog article, we will explore the causes of shoulder pain and discuss some effective treatment options.
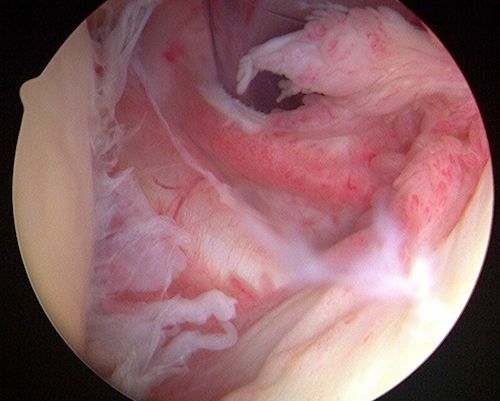
Table of contents
Causes of Shoulder Pain
There many different conditions that can present with shoulder pain.
Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff consists of a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and facilitating movement. Overuse, repetitive motions, trauma, or aging can lead to rotator cuff tears or strains, causing pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
Cuff tendonitis - Impingement syndrome
This occurs when the rotator cuff tendons become irritated or inflamed, often due to repetitive overhead activities. Shoulder impingement causes pain when raising the arm and can result in bursitis or tendonitis.
Frozen shoulder
Frozen shoulder is characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. The exact cause is unknown, but it often develops after an injury or prolonged immobilization. People with diabetes or thyroid disorders are more prone to developing frozen shoulder.
Shoulder arthritis
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the shoulder joint, leading to chronic pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Arthritis typically worsens over time and may require a combination of non-surgical and surgical interventions.
Shoulder instability
Shoulder instability occurs when the joint's structures, including ligaments and tendons, are unable to keep the humeral head (upper arm bone) securely within the shoulder socket. This can result in recurrent dislocations, causing pain and instability.
Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis is caused by calcium deposits in the rotator cuff tendons, especially the supraspinatus. Exact cause remains unknown. It can cause intense pain, especially at night.
Shoulder fractures
Shoulder fractures may include proximal humerus fractures, clavicle fractures, scapula fractures, ACJ separations, etc.
Shoulder pain - Diagnosis
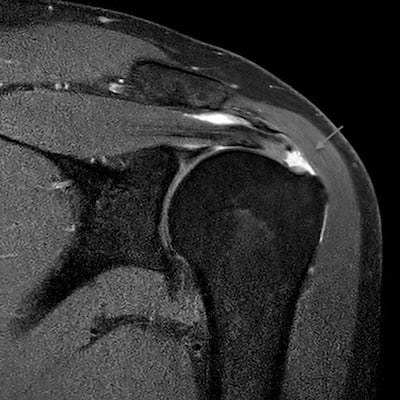
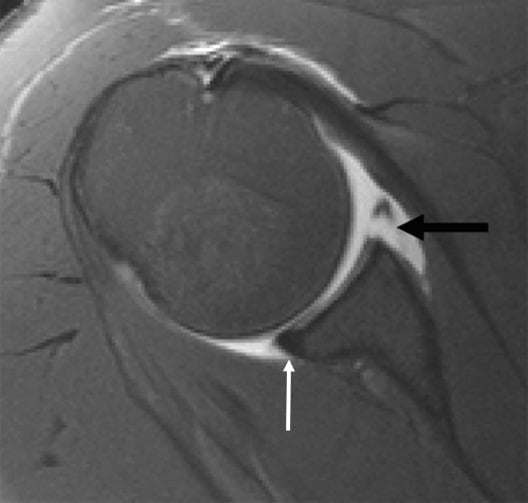
The doctor will begin the diagnostic approach with history taking and physical examination. The doctor will assess the range of motion and perform specific clinical tests for any possible condition. He will then perform an ultrasound of the area and order some further imaging tests depending on the possible underlying disease, such as X-rays and MRIs.
Shoulder pain - Treatment
Treatment options for shoulder pain may include:
1. Rest and Activity Modification: In many cases, shoulder pain can be managed with rest, avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain or strain the shoulder. Modifying your daily activities and using proper ergonomics can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
2. Physical Therapy: A tailored physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, improve range of motion, and alleviate pain. Physical therapists use various techniques, including exercises, stretches, and manual therapy, to promote healing and restore function.
3. Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation in the shoulder joint. However, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.
4. Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. These injections are usually combined with other conservative treatments like physical therapy.
5. Surgical Intervention: If conservative treatments fail to alleviate shoulder pain or if the condition is severe, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include arthroscopy, rotator cuff repair, shoulder replacement, or stabilization procedures, depending on the underlying cause of the pain.
Shoulder pain - prevention
Preventing shoulder pain involves maintaining good posture, practicing proper lifting techniques, and avoiding repetitive overhead activities. Regular exercise to strengthen the shoulder muscles and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of shoulder injuries.
Shoulder pain can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. It is important to seek medical attention if shoulder pain persists or worsens despite conservative measures. An orthopaedic specialist can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan to address the underlying cause of the pain.
Remember, each case of shoulder pain is unique, and treatment options may vary. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for an individualized approach to managing shoulder pain effectively.
Underestimating the problem may lead to unnecessary delays, or lead to chronic issues that can become more difficult to eradicate. Please contact us to receive timely & personalised treatment for your pain.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What are the causes of shoulder pain?
– Impingement syndrome & Rotator cuff tears
– Dislocation/Instability
– Calcific tendonitis
– Fractures
– Arthritis
– Frozen shoulder
When should I see a doctor?
– Acute injury with severe pain
– Pain not mitigated by painkillers
– Night pain that disturbs sleep
– Pain that disrupts activities of daily living
Find us
Book an appointment with us today

