Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon

Table of contents
Knee pain is very common and can have a significant impact on our activities of daily living. Knee pain can be caused by injuries, overuse, or an underlying process, such as arthritis.Treatment depends on the underlying pathology.

Knee pain: Anatomy
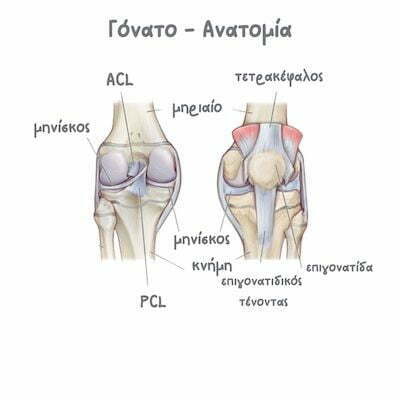
The knee is a vulnerable joint that is put under a lot of stress by everyday activities. The knee joint includes the femur, tibia, fibula & patella.
These bones are connected to each other by four main ligaments, which stabilize the joints:
- Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
- Medial & lateral collateral ligaments
Bones are covered by articular cartilage. Articular cartilage reduces friction between bones and evenly distributes loads during movement.
Between the articulating bones are the menisci (medial meniscus and external meniscus), which act as "shock absorbers", absorbing vibrations during movement.
Causes
Many knee conditions are the result of the normal wear and tear of the articular cartilage. In other cases, knee problems are the result of an injury.
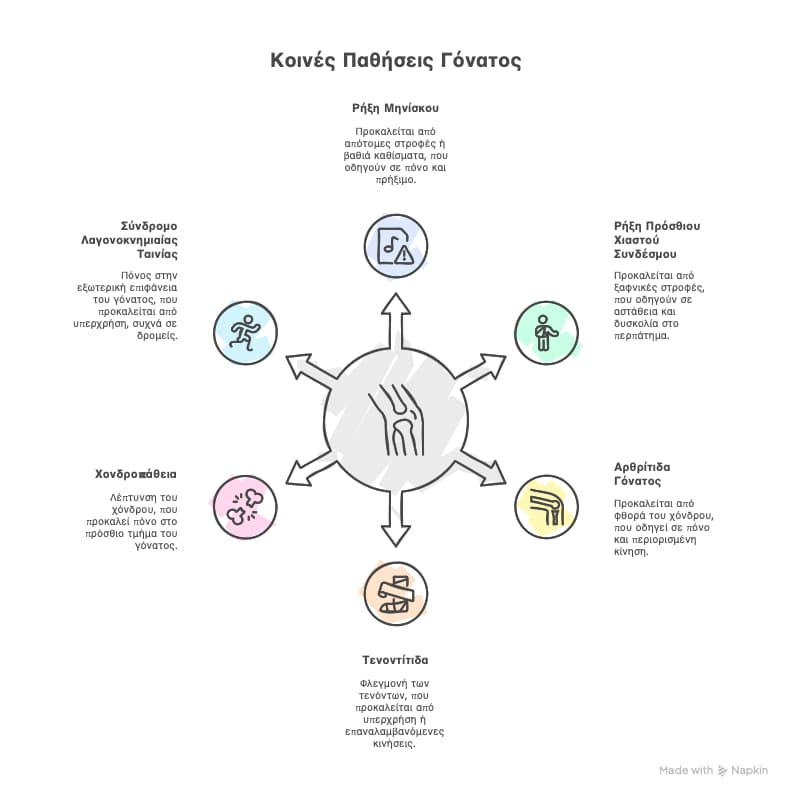
- Meniscal Tearscaused during sharp twisting movements or squatting. Symptoms include pain, swelling and inability to move the knee. Sometimes a characteristic"crack"sound is heard during the injury. Patients with a meniscal tear and mechanical symptoms or a locked knee require surgical repair with arthroscopy for meniscectomy or meniscal repair.
- ACL tears: usually caused by a sudden turn of the knee, eg a sudden change of direction. Symptoms include pain, swelling, unsteadiness and difficulty walking. Patients with persistent knee instability after a cruciate tear require arthroscopic reconstruction of the ligament.
- Knee arthritis: the cartilage in the joints wears down, causing pain and difficulty in movement. It affects older people.
- Tendonitis: inflammation of the tendons around the knee. The patellar tendon and hamstrings are often involved.
- Chondropathy: It occurs most often in the kneecap and is due to the thinning and wear of the cartilage. Patients with chondropathy experience anterior knee pain that is worse when going up and down stairs.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Pain on the outer surface of the knee due to inflammation from overuse. It occurs more often in runners.
Diagnosis
In addition to a complete medical history and physical examination, the diagnostic approach to knee problems may include x-rays, ultrasound & MRI. Dr. Panagopoulos will take a detailed history & examine the knee. Then, depending on the circumstances & clinical suspicion, he will request the required imaging test to confirm the diagnosis & determine the appropriate treatment.

Prevention & treatment
Factors that may help alleviate or prevent knee pain include:
- Warming up and stretching before exercise.
- Strengthening the muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps.
- Body weight maintenance.
- Avoiding smoking. It is proven that smoking contributes to the onset of osteoarthritis and the deterioration of articular cartilage.
- Rest, ice, and elevation of the limb may help with a minor injury or mild inflammation.
- In some cases, hyaluronic acid or biological agents may alleviate pain for a reasonable period of time.
If conservative treatment fails, then your orthopedic surgeon may recommend surgical treatment of the condition, depending on the extent of the condition and your symptoms. Surgical treatment may be done with knee arthroscopy that offers a definitive solution with excellent functional results. In cases of advanced arthritis, open surgery with knee replacement might be needed.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of knee pain?
– Meniscal tears
– ACL/PCL tears
– Knee arthritis
– Cartilage damage
– Kneecap instability problems
– Ligament injury & tendonitis
– Iliotibial band syndrome
What does the diagnostic approach involve?
– History & clinical exam
– X-rays
– MRI
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
