Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon
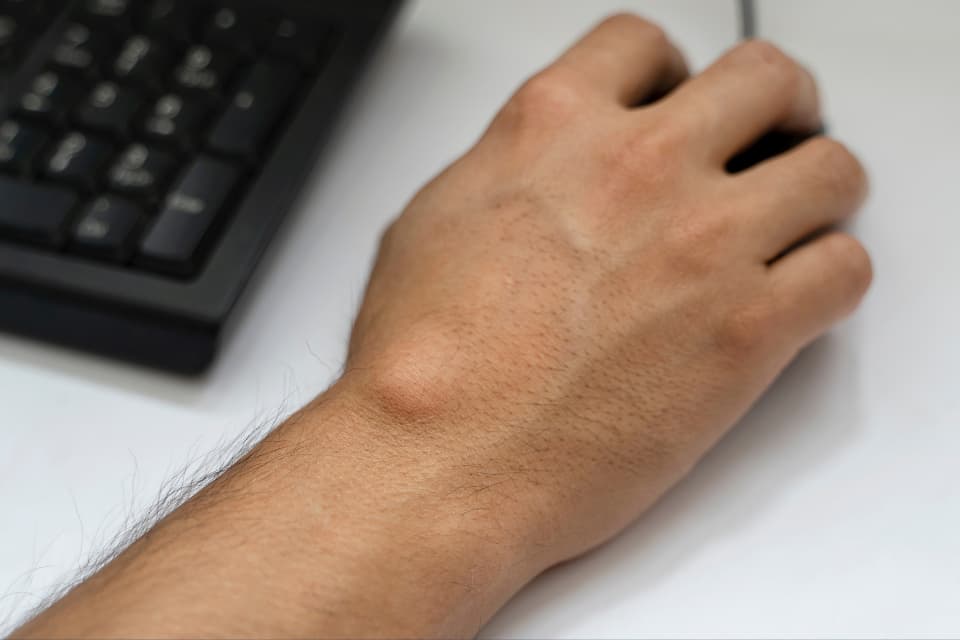

Table of contents
What is a ganglion cyst?
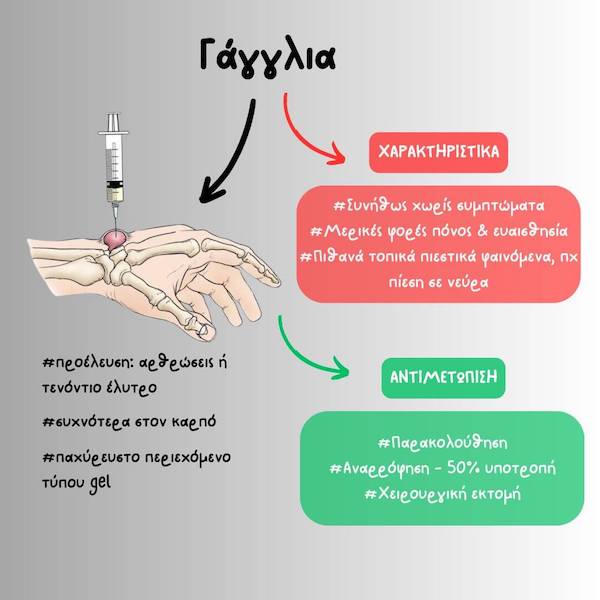
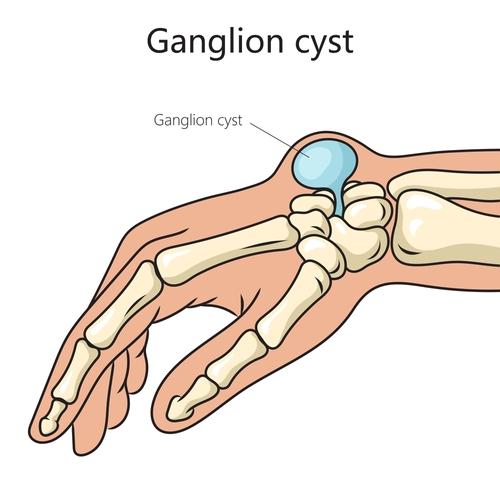
To γάγγλιο είναι μία μικρή κύστη που εμφανίζεται κάτω από το δέρμα. Είναι πιο συχνό σε ασθενείς 20-50 ετών, αν και μπορεί να εμφανιστεί σε κάθε ηλικία, και εκδηλώνεται συνήθως στον καρπό ή το χέρι. Η κύστη περιέχει παχύρευστο υγρό αρθρικής προέλευσης, με χαρακτηριστική υφή τύπου gel. Το γάγγλιο συνήθως προέρχεται είτε από μια άρθρωση είτε από το περίβλημα (έλυτρο) ενός τένοντα.
What causes ganglion cysts?
Ganglion cysts are very common. The exact cause is not known; however, they are thought to be related to repetitive microinjury of the involved joint capsule, that causes a defect or a soft spot through which material can bulge out. Some of the risk factors that have been implicated include age (20-50), sex (F>M), previous injuries or repetitive tasks, arthritis.
Ποιοι είναι οι συνηθέστεροι τύποι;
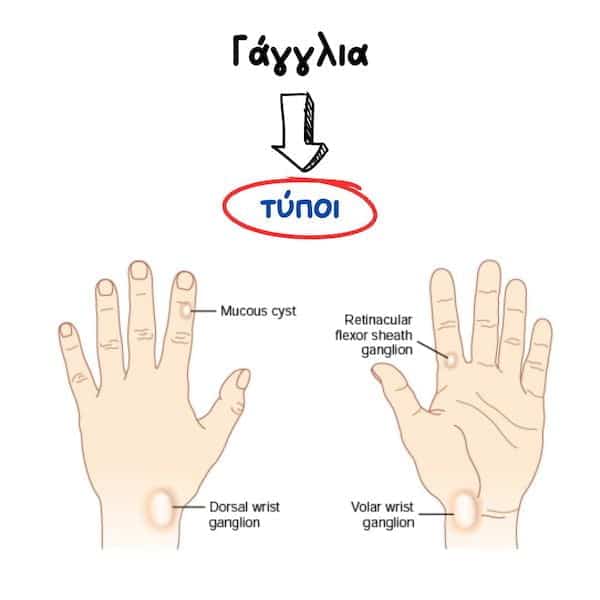
Υπάρχουν διάφορα είδη, ανάλογα με την περιοχή. Τα περισσότερα βρίσκονται στο χέρι και τον καρπό, αν και μπορεί να εμφανιστούν και σε αρθρώσεις σε άλλα σημεία του σώματος (ακρωμιοκλειδική, ποδοκνημική, πόδι, γόνατο). Οι κυριότεροι είναι οι εξής:
- Dorsal wrist ganglion: they arise in the back of the wrist; these are the most common type. They arise from the scapholunate ligament.
- Volar wrist ganglion: this is found in the front of your wrist. Sometimes, it can be in close proximity to the radial artery, which needs attention during removal.
- Βλεννώδης κύστη (mucous cyst): βρίσκεται στη ραχιαία επιφάνεια της τελικής άρθρωσης των δακτύλων και σχετίζεται με υποκείμενη αρθρίτιδα.
- Retinacular cyst: typically derive from the tendon sheath of a flexor tendon, in one of fingers
What are the symptoms of ganglion cysts?
The first sign of a ganglion is the appearance of a lump in the wrist or hand. This may vary in size. Most of the time, it does not hurt at all and it only causes a cosmetic issue. Other times it can cause pain and inflammation, by mass effect.
Diagnosis
Η διάγνωση είναι συνήθως προφανής κατά την κλινική εξέταση. Το γάγγλιο είναι συνήθως ευκίνητο και δεν συμφύεται με το υπερκείμενο δέρμα. Η κάμψη του καρπού κάνει ένα ραχιαίο γάγγλιο πιο εμφανές. Ο ιατρός μπορεί να βάλλει μια φωτεινή πηγή δίπλα στο οζίδιο, προκειμένου να διαπιστώσει αν το περιεχόμενο είναι υγρό (transillumination). Στη συνέχεια, ο γιατρός θα εξετάσει τα νεύρα του άνω άκρου και θα βεβαιωθεί ότι το γάγγλιο δεν πιέζει κάποια ευγενή δομή.
Ο ιατρός μπορεί να σας παραπέμψει για μια απλή ακτινογραφία του χεριού ή του καρπού, προκειμένου να αναζητηθούν συνοδές παθήσεις, όπως υποκείμενη αρθρίτιδα. Ο υπέρηχος ή η μαγνητική τομογραφία επιβεβαιώνουν την διάγνωση, ή παρέχουν περαιτέρω πληροφορίες, αν υπάρχουν γειτονικές ευαίσθητες δομές (πχ, κερκιδική αρτηρία), ή αν η διάγνωση τίθεται υπό αμφισβήτηση.

Conservative treatment
Η συντηρητική θεραπεία περιλαμβάνει τα εξής:
- Simple παρακολούθηση. Ενίοτε ένα γάγγλιο μπορεί να απορροφηθεί μόνο του με τον καιρό. Επίσης μπορεί να σπάσει μετά από κάποιον τυχαίο τραυματισμό και να εξαφανιστεί.
- Activity modification - avoid activities that cause pain
- Ακινητοποίηση σε κηδεμόνα – νάρθηκα καρπού για μικρό χρονικό διάστημα
- Παρακέντηση με βελόνα, με ή χωρίς έγχυση κορτιζόνης
Το ποσοστό υποτροπής για την παρακέντηση με βελόνα είναι γύρω στο 50%. Παρά το γεγονός αυτό, πολλοί είναι οι ασθενείς που επιλέγουν την παρακέντηση για προσωρινή ανακούφιση από τα συμπτώματα, μέχρι να βρουν το κατάλληλο timing για το χειρουργείο, ή να το πάρουν απόφαση. Η παρακέντηση γίνεται γρήγορα στο ιατρείο, υπό τοπική αναισθησία.
Surgical Treatment
Αν η συντηρητική θεραπεία αποτύχει, ή ο ασθενής παρουσιάζει πόνο, ενόχληση, ή κοσμητικό πρόβλημα, υπεισέρχεται η χειρουργική θεραπεία. Η χειρουργική θεραπεία περιλαμβάνει την εκτομή του γαγγλίου υπό τοπική αναισθησία. Είναι σημαντικό να αφαιρεθεί όλο το γάγγλιο μαζί με το τμήμα του αρθρικού θυλάκου από το οποίο προέρχεται, έτσι ώστε να ελαχιστοποιηθεί η πιθανότητα υποτροπής. Μετά την αφαίρεση, τοποθετείται μία περίδεση γύρω από την περιοχή. Συνιστάται ξεκούραση για 1-2 εβδομάδες, με ήπια κινητοποίηση προκειμένου να αποφευχθεί τυχόν δυσκαμψία.
Σε ορισμένες περιπτώσεις, είναι προτιμότερο η χειρουργική εξαίρεση να λαμβάνει χώρα υπό μέθη ή γενική αναισθησία, όπως σε περίπτωση υποτροπής, παλαμιαίου γαγγλίου (λόγω εγγύτητας με την κερκιδική αρτηρία), ή αν αυτό αποτελεί προτίμηση του ίδιου του ασθενούς. Σε επιλεγμένες περιπτώσεις, το χειρουργείο μπορεί να πραγματοποιηθεί αρθροσκοπικά (αρθροσκόπηση καρπού), με παρόμοια αποτελέσματα.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a ganglion cyst?
Είναι μία κύστη κάτω από το δέρμα και περιέχει υγρό αρθρικής προέλευσης, με χαρακτηριστική υφή τύπου gel. Εκδηλώνεται συνήθως στον καρπό ή το χέρι.
Which are the most common locations?
– Ραχιαίο (το πιο συχνό)
– Παλαμιαίο (λιγότερο συχνό, αλλά κοντά σε ευαίσθητες δομές, όπως η κερκιδική αρτηρία)
– Βλεννώδης κύστη (mucous cyst – συνδέεται με αρθρίτιδα της τελικής φάλαγγας των δακτύλων)
– Στο έλυτρο τενόντων (retinacular cyst), πιο συχνά των καμπτήρων των δακτύλων του χεριού.
What's the treatment?
– Απλή παρακολούθηση, ενίοτε η κύστη μπορεί να απορροφηθεί μόνη της.
– Παρακέντηση +/- ένεση κορτιζόνης εντός της κύστης (υποτροπή ~50%).
– Εκτομή υπό τοπική αναισθησία.
– Εκτομή με μέθη ή γενική αναισθησία, σε ορισμένες περιπτώσεις (γειτνίαση με ευαίσθητες δομές).
Τα γάγγλια εμφανίζονται μόνο στο χέρι και τον καρπό;
Όχι, ένα γάγγλιο μπορεί να εμφανιστεί σε οποιαδήποτε άρθρωση του σώματος, πχ στον αγκώνα ή στην ακρωμιοκλειδική άρθρωση σε συνδυασμό με υποκείμενη αρθρίτιδα, στο γόνατο πλησίον μιας ρήξης μηνίσκου, κλπ.
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
