Shoulder tendonitis | Diagnosis & treatment
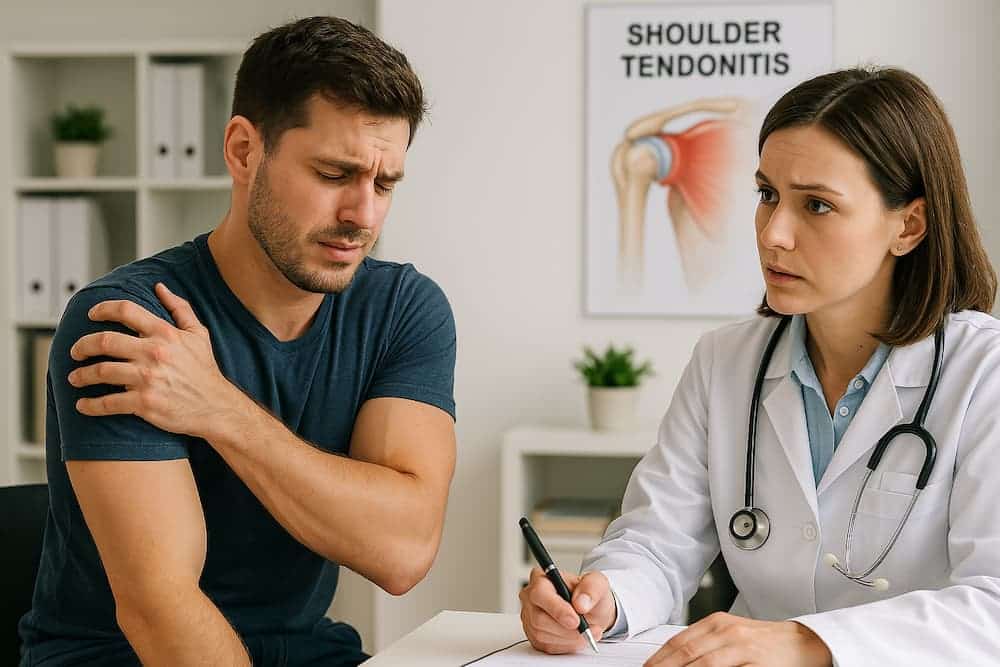
Shoulder tendonitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the rotator cuff or biceps tendon, often resulting from repetitive overhead movements or structural impact. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, while discussing its relationship to impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tears.
Table of contents
What is shoulder tendonitis?
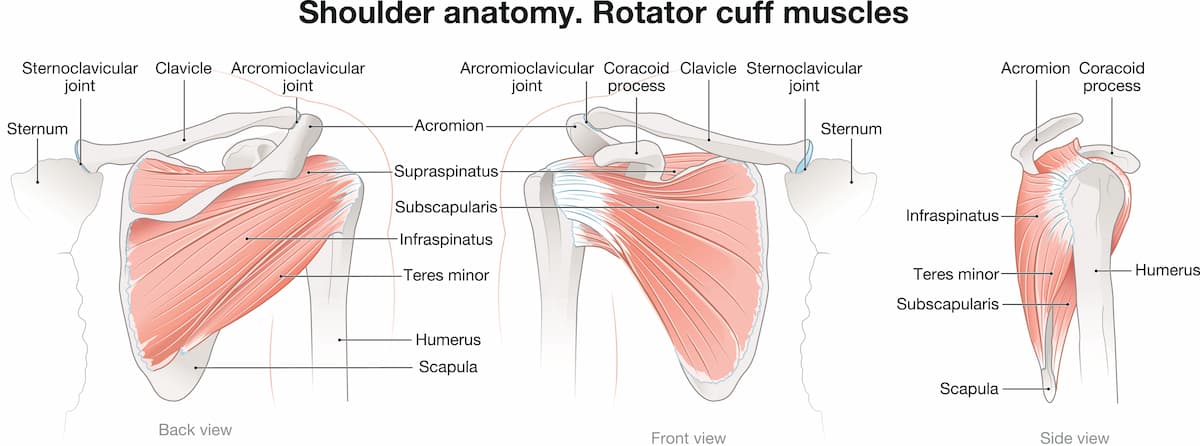
Η τενοντίτιδα ώμου είναι η φλεγμονή των τενόντων που συνδέουν τους μύες του στροφικού πετάλου (υπερακάνθιος, υποακάνθιος, έλασσων στρογγύλος και υποπλάτιος) με την κεφαλή του βραχιονίου. Αυτοί οι τένοντες σταθεροποιούν την άρθρωση του ώμου και διευκολύνουν την κίνηση. Όταν παρουσιάζουν φλεγμονή, οι τένοντες παχύνονται και μπορεί να υφίστανται παγίδευση κάτω από το ακρώμιο (μια οστική προεξοχή της ωμοπλάτης), οδηγώντας σε πόνο και περιορισμένη κινητικότητα. Αυτή η τελευταία κατάσταση είναι γνωστή και ως impingement syndrome ώμου, ή σύνδρομο υπακρωμιακής προστριβής. Πιο συχνή είναι η τενοντίτιδα υπερακανθίου.
Causes & risk factors
Causes of shoulder tendonitis – shoulder impingement syndrome include:
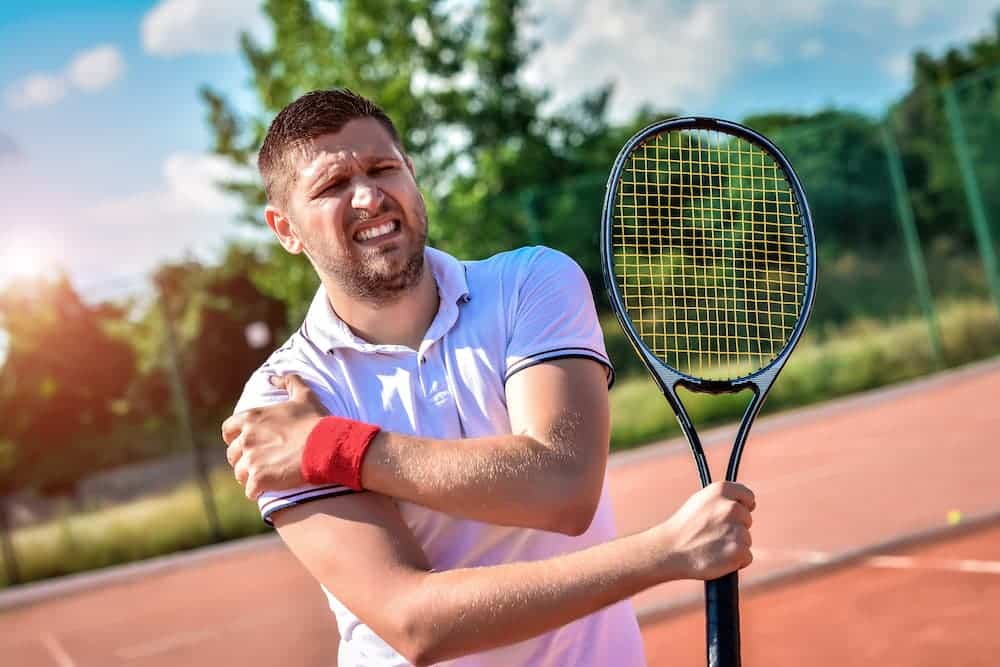
• Επαναλαμβανόμενες κινήσεις πάνω από το κεφάλι: Συχνές σε αθλήματα όπως το μπέιζμπολ, το κολύμπι, το τένις και η άρση βαρών, καθώς και σε επαγγέλματα όπως οι ελαιοχρωματιστές ή οι ξυλουργοί.
• Κακή στάση ή τεχνική: προκαλεί επιπλέον έργο και επιβαρύνει τους τένοντες.
• Age: Οι τένοντες χάνουν την ελαστικότητά τους με την ηλικία, κάνοντάς τους επιρρεπείς σε εκφυλισμό.
• Οξείες κακώσεις: Πτώσεις ή ξαφνικές κινήσεις.
Οι παράγοντες κινδύνου περιλαμβάνουν:
- Αθλήματα που σχετίζονται με επαναλαμβανόμενη κίνηση, όπως κολύμπι, τένις, ή volley
- Εργασίες που προϋποθέτουν επαναλαμβανόμενη κίνηση πάνω από το κεφάλι
- Οι δουλειές καθαριότητας του σπιτιού
- Υποκείμενες παθήσεις που προκαλούν stress στον τένοντα, όπως αρθρίτιδα ή διαβήτης
- Το ακατάλληλο ζέσταμα πριν από την προπόνηση

Symptoms
Τα συμπτώματα της τενοντίτιδας ώμου περιλαμβάνουν:
- Πόνος στον ώμο κατά τη διάρκεια δραστηριοτήτων πάνω από το επίπεδο των ώμων (π.χ. φθάνοντας ένα ράφι ή ένα ντουλάπι, χτένισμα).
- Νυχτερινός πόνος στον ώμο, που διαταράσσει την ποιότητα του ύπνου
- Δυσκαμψία και αδυναμία του άκρου
Οι ρήξεις του στροφικού πετάλου (μερικές ή ολικές, συνήθως ρήξη υπερακανθίου) μπορεί να προκαλέσουν οξύ πόνο και σημαντική αδυναμία. Η ρήξη τένοντα ώμου συχνά αναπτύσσεται σαν εξέλιξη μετά από χρόνια τενοντίτιδα ή οξύ τραύμα.
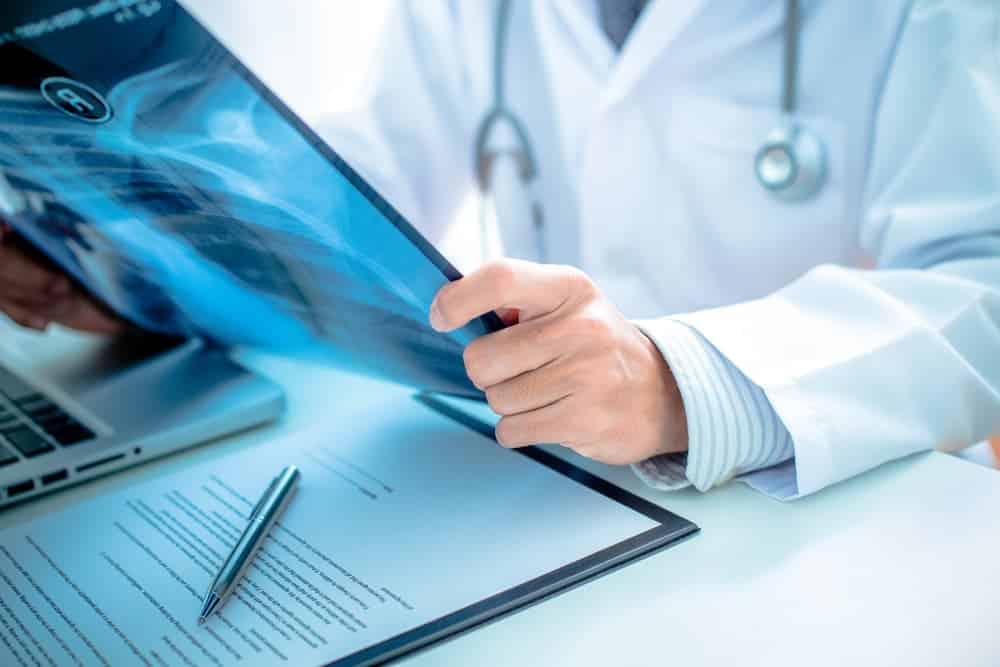
Diagnosis
Dr Panagopoulos will take a full history and perform a detailed physical exam, including measuring range of motion and strength. An x-ray will be ordered to look for arthritis or calcific tendonitis. An ultrasound in the office will be performed to look for tears. An MRI may be ordered to further clarify your anatomy and the extent of the damage, like tear size or degree of muscle atrophy.
Non-surgical treatment
Conservative treatment of rotator cuff tears includes:
- Rest
- Activity modification
- NSAIDS
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Physiotherapy/home exercise program for strengthening and stretching exercises
- Ένεση κορτιζόνης ή PRP
Conservative treatment will help the majority of patients improve their symptoms and overcome shoulder pain, returning to daily activities. If symptoms do not subside, the next option is surgical repair with shoulder arthroscopy.

Surgical treatment
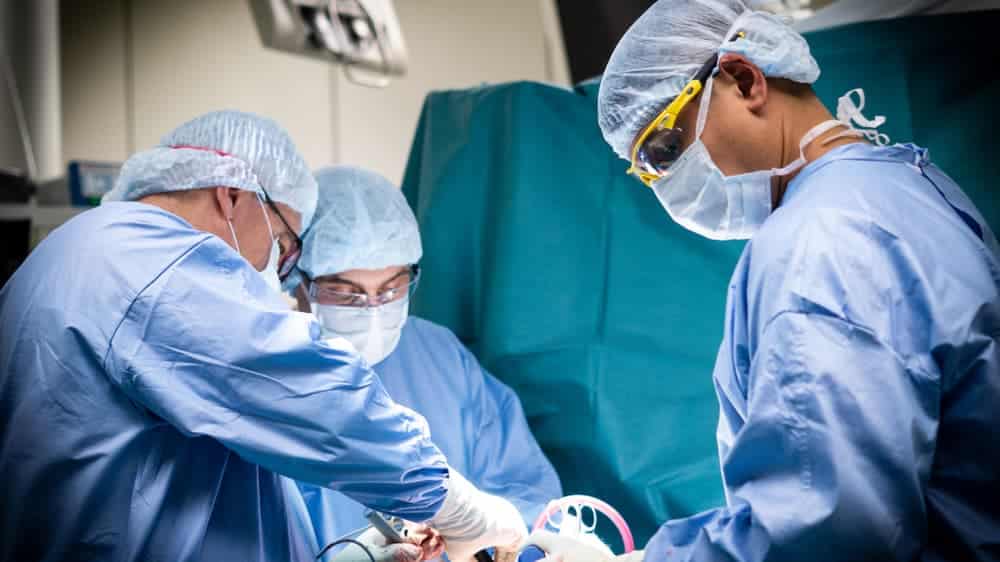
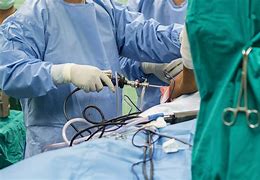
Σε περίπτωση που η συντηρητική θεραπεία δεν προσφέρει τα επιθυμητά αποτελέσματα, το επόμενο βήμα περιλαμβάνει την χειρουργική θεραπεία, με αρθροσκόπηση ώμου. Η αρθροσκόπηση ώμου γίνεται με 3 μικρές οπές 4 χιλιοστών γύρω από τον ώμο, μέσω των οποίων ο χειρουργός εισάγει μια κάμερα και διάφορα εργαλεία.
This is a day procedure. It is performed under general +/- regional anesthetic. You can go home the same day if you wish, just a few hours after the procedure.
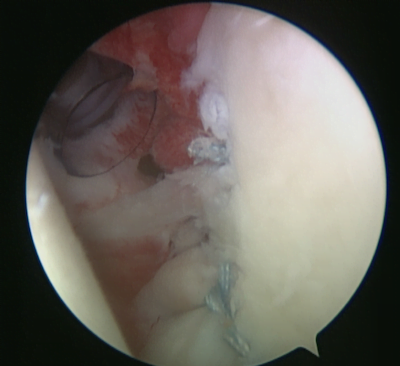
Κατά την αρθροσκόπηση ώμου, πραγματοποιείται χειρουργικός καθαρισμός της φλεγμονής του ώμου και λείανση του ακρωμίου προκειμένου να αυξηθεί ο διαθέσιμος χώρος για τους τένοντες του ώμου και να αποφευχθεί η τριβή. Στην συνέχεια, ο κ. Παναγόπουλος θα επιδιορθώσει τυχόν ρήξεις τένοντα με τη βοήθεια ειδικών ραμμάτων (άγκυρες).
Η αρθροσκόπηση ώμου προσφέρει άριστα αποτελέσματα με εξαιρετικά χαμηλό ποσοστό επιπλοκών και προσιτό κόστος. Ο ασθενής εξέρχεται από το νοσοκομείο την ίδια μέρα, λίγες ώρες μετά του χειρουργείο. Το άκρο παραμένει σε ανάρτηση για κάποιο διάστημα, ανάλογα με την υποκείμενη παθολογία που αντιμετωπίστηκε. Ο ασθενής αρχίζει στη συνέχεια φυσικοθεραπεία.
Η φυσικοθεραπεία είναι εξαιρετικά σημαντική κατά τη διάρκεια της αποκατάστασης μετά από αρθροσκόπηση ώμου. Ξεκινάει με ήπιες ασκήσεις άμεσα μετεγχειρητικά. Στη συνέχεια ακολουθούν ασκήσεις για την αποκατάσταση του εύρους κίνησης & ενδυνάμωση. Ο χρόνος αποκατάστασης εξαρτάται σε μεγάλο βαθμό από την υποκείμενη παθολογία.
Αν έχετε πόνο στον ώμο, είναι σημαντικό να επισκεφτείτε έναν εξειδικευμένο χειρουργό ώμου. Ο κ. Παναγόπουλος θα συζητήσει μαζί σας όλες τις εναλλακτικές θεραπείες κατά τη διάρκεια της επίσκεψής σας στο ιατρείο.
How effective are cortisone injections against shoulder tendonitis?
Οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης είναι μια κοινή θεραπεία για την τενοντίτιδα ώμου, προσφέροντας σημαντικά βραχυπρόθεσμα οφέλη, προκαλώντας μείωση της φλεγμονής και του πόνου.
Αποτελεσματικότητα των ενέσεων κορτιζόνης
1. Ανακούφιση του πόνου και μείωση της φλεγμονής: Οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης είναι αποτελεσματικές στην ανακούφιση από τον πόνο και στη βελτίωση της λειτουργικότητας του ώμου, μειώνοντας τη φλεγμονή στην πληγείσα περιοχή. Μελέτες δείχνουν ότι μπορούν να προσφέρουν ανακούφιση για αρκετές εβδομάδες έως μήνες.
2. Σύγκριση με άλλες θεραπείες: Οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης είναι γενικά πιο αποτελεσματικές από τα ΜΣΑΦ για βραχυπρόθεσμη ανακούφιση από τον πόνο στην τενοντίτιδα. Ωστόσο, τα μακροπρόθεσμα οφέλη τους είναι λιγότερο σαφή και μπορεί να μην είναι τόσο αποτελεσματικά όσο τα ΜΣΑΦ σε ορισμένες περιπτώσεις.
3. Δόση και διάρκεια: Υψηλότερες δόσεις κορτικοστεροειδών μπορεί να προσφέρουν καλύτερα αποτελέσματα από χαμηλότερες δόσεις, αν και αυτό απαιτεί προσεκτική εξέταση λόγω πιθανών παρενεργειών.
4. Συνδυαστική θεραπεία: Οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης χρησιμοποιούνται συχνά σε συνδυασμό με ασκήσεις φυσικοθεραπείας και αποκατάστασης για την ενίσχυση της ανάρρωσης επιτρέποντας στους ασθενείς να συμμετέχουν σε ασκήσεις χωρίς πόνο.
Πιθανοί κίνδυνοι και επιπλοκές
1. Αποδυνάμωση τενόντων: Οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης μπορεί να αποδυναμώσουν τους τένοντες με την πάροδο του χρόνου, κάτι που προκαλεί ανησυχία για ασθενείς που μπορεί τελικά να χρειαστούν χειρουργική επέμβαση αποκατάστασης στροφικού πετάλου.
2. Χειρουργικές επιπτώσεις: Πρόσφατες μελέτες υποδεικνύουν ότι οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης πριν από τη χειρουργική επέμβαση του στροφικού πετάλου μπορεί να επηρεάσουν αρνητικά την επούλωση της χειρουργικής αποκατάστασης.
3. Παρενέργειες: Αν και γενικά είναι καλά ανεκτές, οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης μπορεί να προκαλέσουν τοπικές παρενέργειες, όπως λέπτυνση ή αποχρωματισμό του δέρματος. Οι συστηματικές επιδράσεις, όπως τα αυξημένα επίπεδα σακχάρου στο αίμα, είναι λιγότερο συχνές αλλά μπορεί να είναι σημαντικές για διαβητικούς ασθενείς.
4. Περιορισμοί συχνότητας: Συνιστάται ο περιορισμός των ενέσεων κορτιζόνης σε όχι περισσότερες από τρεις ετησίως για να ελαχιστοποιηθούν οι κίνδυνοι.
Συνοπτικά, οι ενέσεις κορτιζόνης είναι αποτελεσματικές για τη βραχυπρόθεσμη διαχείριση του πόνου στην τενοντίτιδα του ώμου, αλλά θα πρέπει να χρησιμοποιούνται με σύνεση, λαμβάνοντας υπόψη τον πιθανό αντίκτυπό τους στην υγεία των τενόντων και στα χειρουργικά αποτελέσματα.
What's the role of physiotherapy in shoulder tendonitis?
Η φυσικοθεραπεία παίζει καθοριστικό ρόλο στη θεραπεία της τενοντίτιδας του ώμου, αντιμετωπίζοντας τον πόνο, βελτιώνοντας την κινητικότητα και ενισχύοντας τους μυς γύρω από τον ώμο.
Βασικά πλεονεκτήματα της Φυσικοθεραπείας για την τενοντίτιδα ώμου είναι τα εξής:
1. Ανακούφιση από τον πόνο: Τεχνικές όπως manual therapy, διατάσεις και ο πάγος ή η θερμότητα βοηθούν στη μείωση της φλεγμονής και στην ανακούφιση του πόνου.
2. Ασκήσεις εύρους κίνησης: Συγκεκριμένες διατάσεις και ασκήσεις βελτιώνουν την κινητικότητα των ώμων, αποκαθιστώντας τη φυσική κίνηση χωρίς να επιδεινώνουν την κατάσταση.
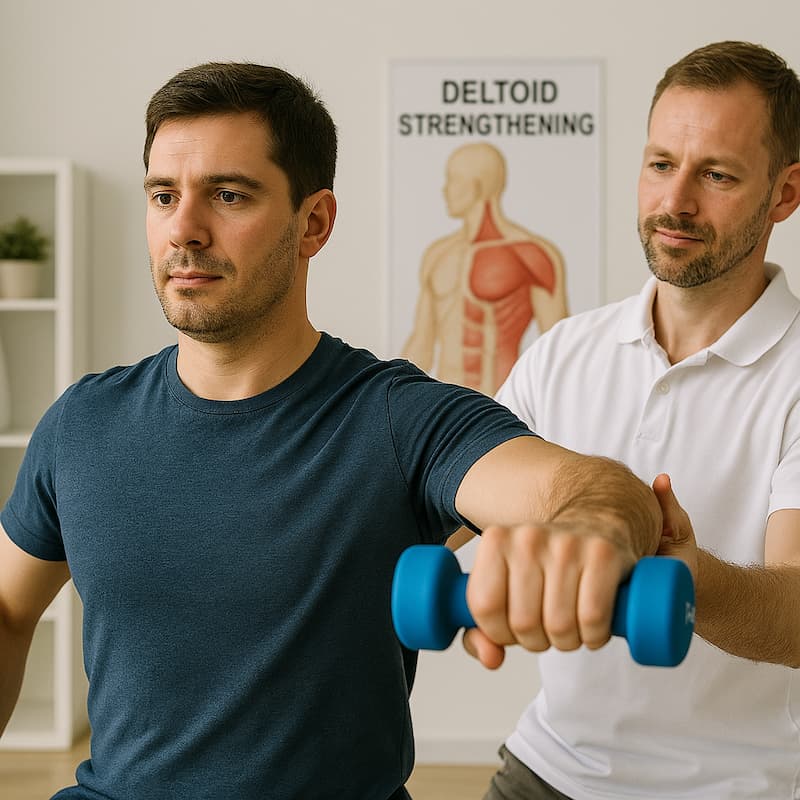
3. Μυϊκή ενδυνάμωση: Η ενδυνάμωση των μυών του στροφικού πετάλου, του δελτοειδή και των σταθεροποιητών της ωμοπλάτης υποστηρίζει την άρθρωση, μειώνει τον μελλοντικό κίνδυνο και ενισχύει τη συνολική λειτουργία.
4. Κινητοποίηση και σταθεροποίηση της άρθρωσης: Τεχνικές για την αποκατάσταση της κινητικότητας και της σταθερότητας των αρθρώσεων, διασφαλίζουν τη σωστή κίνηση και μειώνουν την καταπόνηση των τενόντων.
5. Εκπαίδευση και πρόληψη: Οι φυσιοθεραπευτές παρέχουν καθοδήγηση σχετικά με την σωστή τροποποίηση των δραστηριοτήτων, τη σωστή μηχανική του σώματος και τις ασκήσεις στο σπίτι για την πρόληψη της υποτροπής.

Οφέλη της Φυσικοθεραπείας
• Μη χειρουργική προσέγγιση: Συχνά αποφεύγει την ανάγκη για χειρουργική επέμβαση βελτιώνοντας τη λειτουργία και μειώνοντας τον πόνο με συντηρητικά μέσα.
• Εξατομικευμένα Σχέδια Θεραπείας: Προσαρμοσμένα στη συγκεκριμένη κατάσταση και τους στόχους του ασθενούς, εξασφαλίζοντας αποτελεσματική ανάρρωση.
• Προ και μετεγχειρητική υποστήριξη: Ενισχύει την ανάρρωση πριν και μετά την επέμβαση βελτιώνοντας τη δύναμη και την ευλυγισία.
Χρονοδιάγραμμα αποκατάστασης
Οι περισσότεροι ασθενείς βλέπουν σημαντική βελτίωση εντός 6-12 εβδομάδων συνεπούς φυσικοθεραπείας, με την έγκαιρη παρέμβαση και την τήρηση προγραμμάτων άσκησης να αποτελούν βασικούς παράγοντες για την ταχύτητα αποκατάστασης και την πρόληψη της υποτροπής.
τενοντίτιδα ώμου ασκήσεις
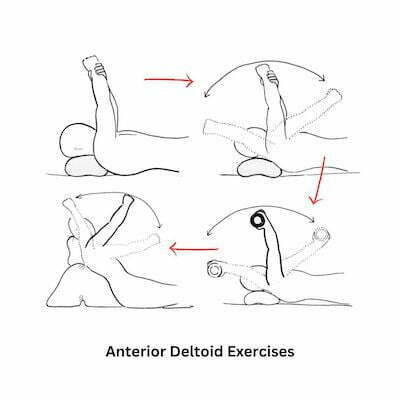
Η συντηρητική θεραπεία είναι το πρώτο βήμα στην τενοντίτιδα ώμου – σύνδρομο πρόσκρουσης ώμου. Συνήθως μερικές συνεδρίες φυσικοθεραπείας, μαζί με ασκήσεις στο σπίτι και ενδεχομένως μία ένεση κορτιζόνης, είναι ικανές να βελτιώσουν δραματικά τον πόνο στον ώμο και να μας επιτρέψουν μια απρόσκοπτη επιστροφή στη καθημερινότητα. Η κλινική μας ενθαρρύνει ασκήσεις για την ενδυνάμωση του πρόσθιου δελτοειδούς, όπως ενδεικτικά οι παρακάτω.

FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What is shoulder tendonitis?
Shoulder tendonitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons, often resulting from repetitive overhead movements or structural impact.
How is shoulder tendonitis managed?
– Physiotherapy/home exercise program
– Cortisone or PRP injections
– Shoulder arthroscopy
Πόσος καιρός χρειάζεται για να περάσει η τενοντίτιδα ώμου?
Εξαρτάται από πολλούς παράγοντες, όπως την βαρύτητα της πάθησης και την προσήλωση του ασθενούς στη θεραπεία. Ήπιες περιπτώσεις μπορεί να βελτιωθούν σημαντικά σε 1-2 εβδομάδες, ενώ πιο βαριές τενοντίτιδες μπορεί να χρειαστούν εντατική θεραπεία και μερικούς μήνες.
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
Shoulder tendonitis | Diagnosis & treatment Read More »