Georgios Panagopoulos MD | Orthopaedic Surgeon
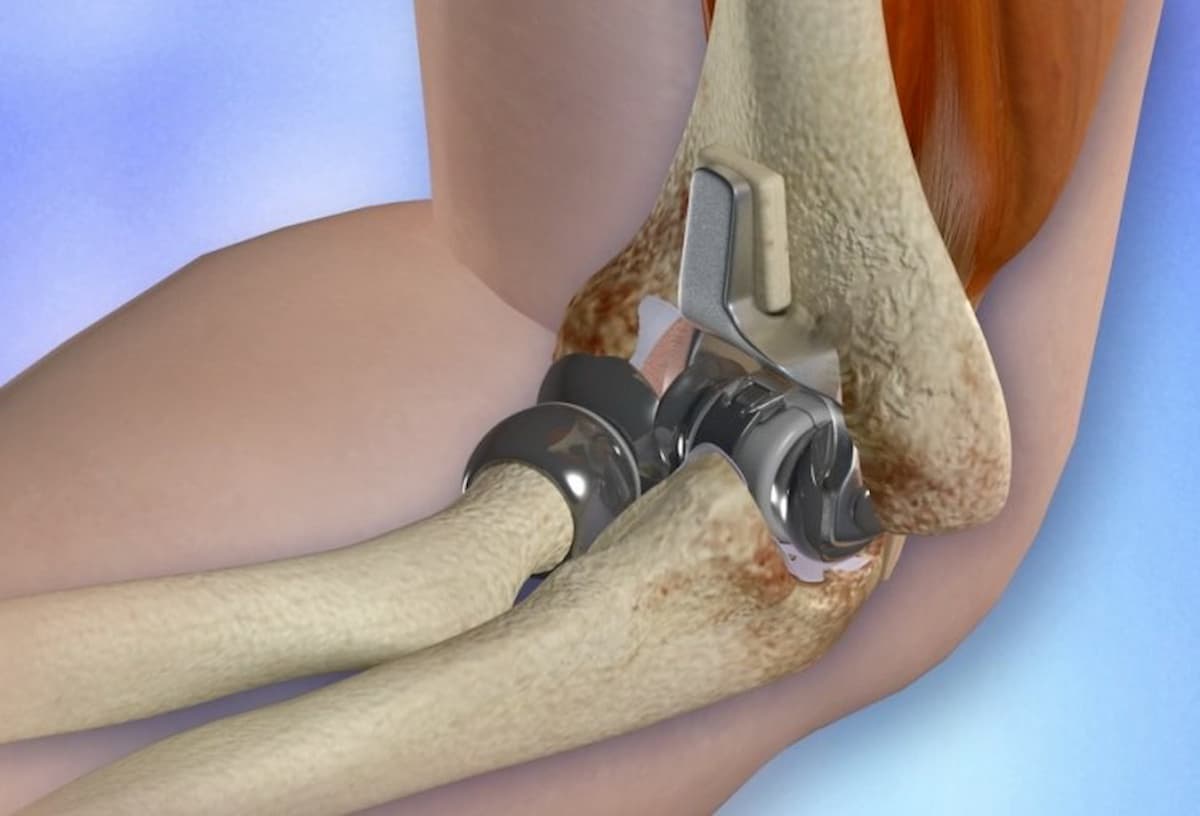
Table of contents
What is elbow arthroplasty?
The elbow joint is where your arm bone (humerus) connects to the 2 bones of your forearm (radius and ulna). The elbow joint is like a hinge. Elbow arthroplasty, also called elbow replacement, is a surgical procedure that replaces the damaged parts of your bones in the elbow with implants made of metal and plastic, with the intent to relieve pain and restore function at the level of the elbow. The 2 main types are total elbow arthroplasty and elbow hemiarthroplasty. Total elbow arthroplasty involves replacement of all the bony surfaces of the joint. The articulation between the components is artificial. A partial elbow replacement or hemiarthroplasty is when only one surface of the joint is replaced, typically the humeral side, such that the implant articulates with the opposing native bone. A hemiarthroplasty is most often performed in trauma, typically distal humerus fractures that are very distal. These fractures can be very closed to the joint line and are often not amenable to reconstruction with plates and screws. In arthritis where the whole joint is affected, a total elbow replacement is more appropriate. Most total elbow replacements are nowadays linked. This is usually a sloppy hinge, meaning that some sideways movement is still allowed by the implant. This design has been shown to have lower loosening rates. The surgeon will recommend the type of elbow replacement you need on an individualized basis.
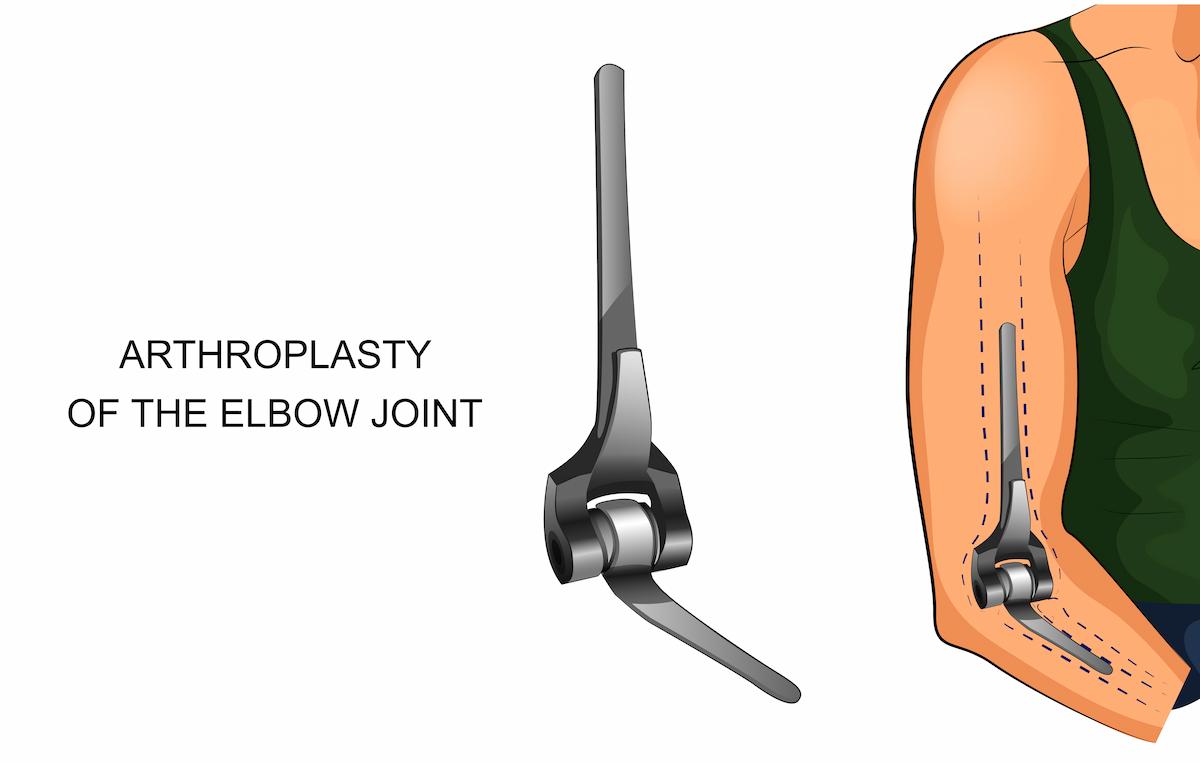
Why do I need an elbow arthroplasty?
Conditions that may require an elbow arthroplasty include:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Other inflammatory arthropathies
- Post-traumatic arthritis
- Trauma: certain fractures of the distal humerus, especially those that are very close to the joint, may not be reconstructable with plates and screws.
What happens before the procedure?
Before elbow arthroplasty, you will typically undergo preoperative assessment. You will be asked about your health history in detail. You will be asked to bring along a full list of your medications. You may need to stop taking some of your medications a few days before surgery (especially blood thinners). Before the procedure, you may also need blood tests, a chest x-ray and an ECG (electrocardiogram) or cardiology consult, to make sure it’s safe to proceed with surgery. The anaesthetist will give you specific preoperative instructions, including how long before surgery to stop eating and drinking. Typical recommendations usually suggest no eating or drinking at least six hours prior to surgery. Your surgeon will usually ask you to have a CT scan of the affected elbow for preoperative planning.
Admission to hospital - Anaesthesia
Admission to hospital occurs the day of surgery. Elbow arthroplasty is performed under general anesthesia +/- regional nerve block, which provides pain relief postoperatively for 12-18 hours. Be prepared to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days.
What happens during the procedure?
Most people get a general anaesthetic together with a nerve block (interscalene block). The general anaesthetic will put you to sleep, and the nerve block will numb your whole arm for 12-18 hours. This also provides excellent postoperative analgesia (pain relief). During the procedure you will lie on the opposite side (lateral position) and a tourniquet will be applied high on your arm. The surgeon performs a 15-cm incision on the back of your elbow and then finds and protects your ulnar nerve. The ligaments around the elbow are released and the bone is exposed and prepared with special jigs. The final implants are secured with bone cement, which sets hard within 1 minutes or so. The tissues and skin are then repaired, and a dressing is applied. Your arm is placed in a sling. The patient wakes up and is moved to recovery.
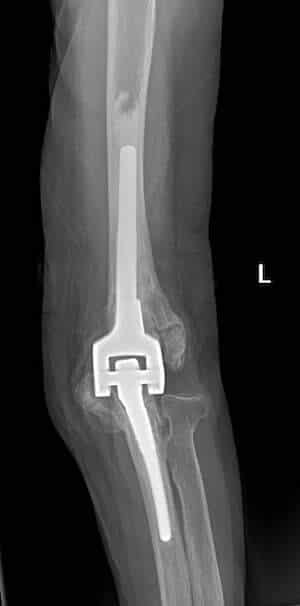
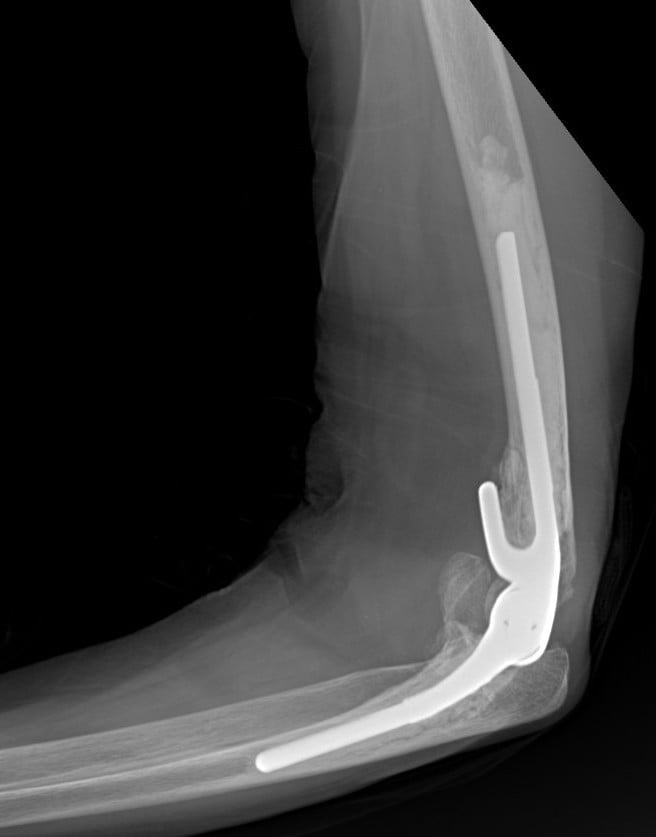
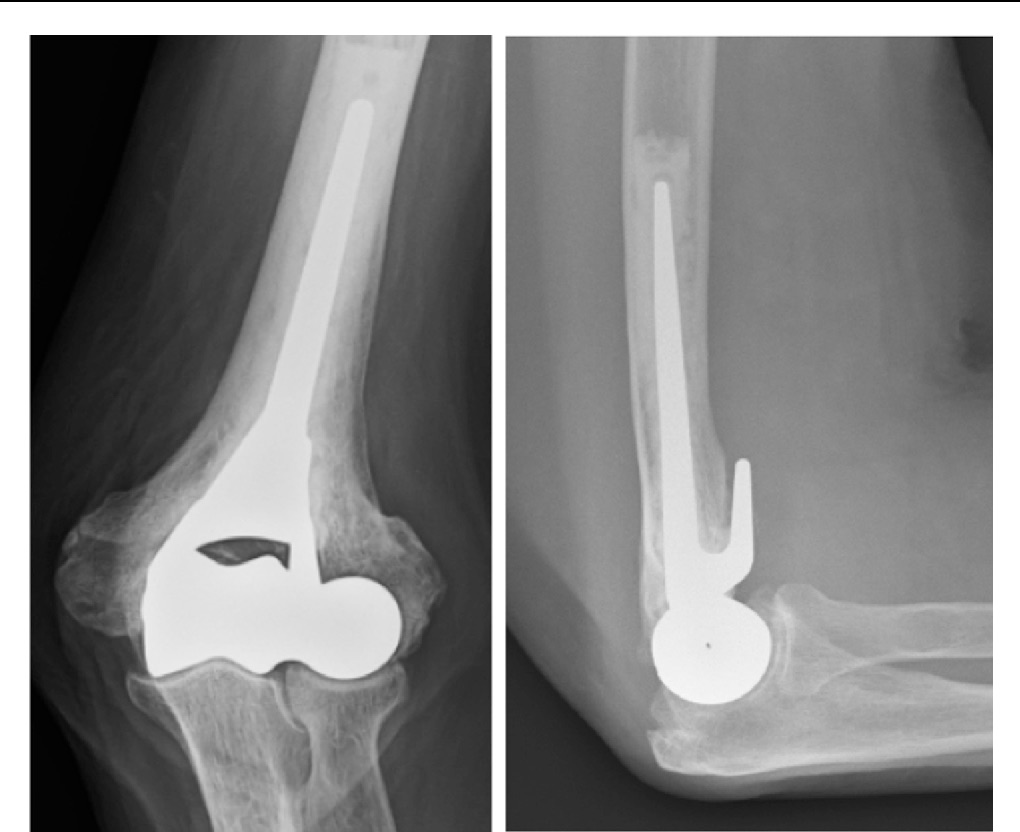
What to expect after the procedure?
Most people stay in hospital for 1 or 2 nights after an elbow arthroplasty. A postoperative x-ray is typically ordered prior to discharge. Early mobilization is paramount for a successful outcome. Your doctor and physiotherapist with build an individualized rehabilitation program for you. Elbow arthroplasty is technically difficult procedure with a number of potential complications and should only be performed by a trained upper limb surgeon. Dr Panagopoulos has extensive experience in complex elbow surgery and will discuss all aspects of the operation with your during your visit in the office.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What is elbow arthroplasty?
Elbow arthroplasty, also called elbow replacement, is a surgical procedure that replaces the damaged parts of your bones in the elbow with implants made of metal and plastic, with the intent to relieve pain and restore function at the level of the elbow.
What are the types of elbow arthroplasty?
The 2 main types are total elbow arthroplasty and elbow hemiarthroplasty.
What are the current indications?
– Osteoarthritis
– Rheumatoid arthritis
– Post-traumatic arthritis
– Very distal or very comminuted distal humerus fractures
Find us
Book an appointment with us today
