Our foot is a complex anatomical structure, consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, 107 ligaments, 19 muscles and tendons. Numerically, the 52 bones of both legs make up 25% of the total 206 bones in our body. Research shows that on average we take 8,000 to 10,000 steps a day.
Foot diseases are among the most common health problems. It is obvious that feet, like other parts of the body, need careful care. And yet, the health of our feet, this important part of the human body, is often overlooked. Here we will talk about some of the most important foot problems.
Table of contents
Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain. Pain from plantar fasciitis is often most noticeable in the morning, during the first few steps after getting out of bed. The plantar fascia is a thick band of tissue on the sole of the foot. Repetitive loading can lead to microtears of the plantar aponeurosis, especially near the heel bone. This micro-tear leads to an inflammatory/healing response, which causes the pain.

Risk factors for plantar fasciitis include: excessive standing, increased body weight, age, recent change in activity level, and stiff calf muscle.Some patients show a characteristic osteophyte (heel spur) on the X-ray, while others have a completely normal X-ray.
Plantar fasciitis can be treated non-surgically in the vast majority of patients. The main components of an effective conservative treatment program are: calf stretches with the knee extended, plantar fascia stretching, activity modification (to avoid hazardous activities), and wearing comfortable shoes. Shockwave therapy is also effective. In extreme cases, surgery may be required.
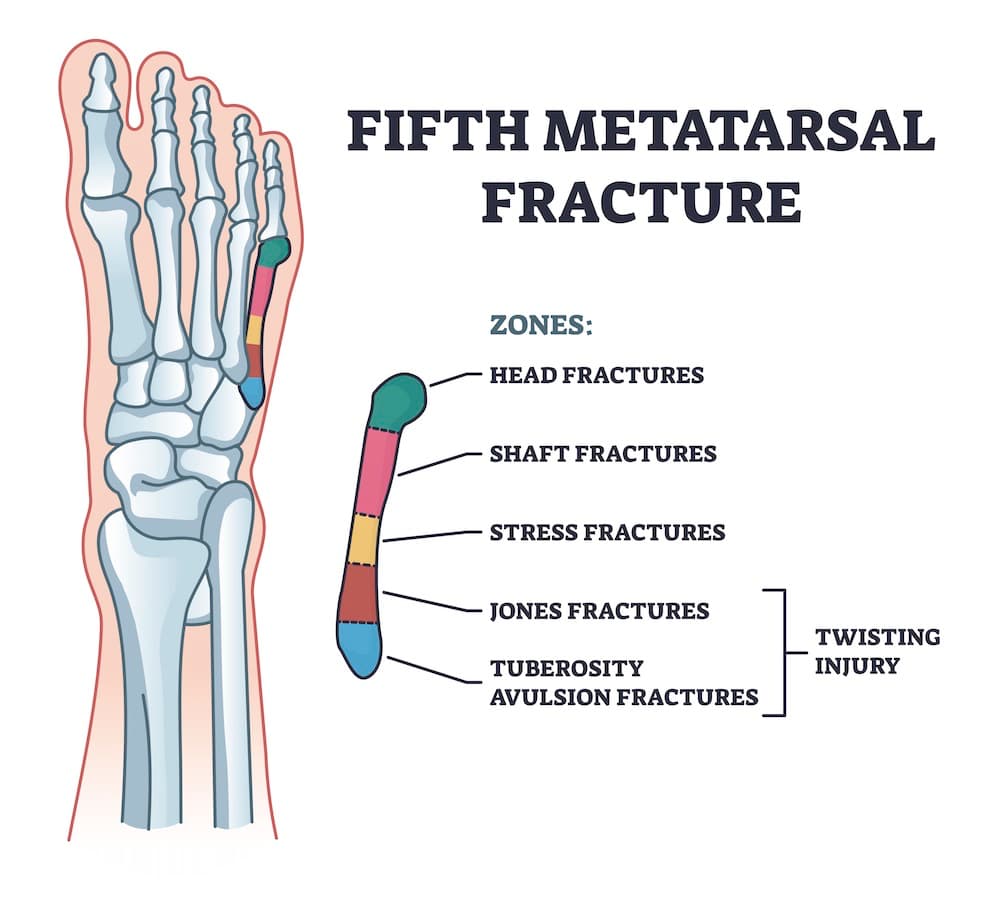
5th metatarsal fracture
The 5th metatarsal is the last bone on the outer surface of the foot. Fracture of the 5th metatarsal is very common in athletes, such as runners, football players, basketball players, who play sports that involve jumping and changing direction. The vast majority of these fractures are treated conservatively, with a boot. An exception are the so-called Jones fractures (zone 2), which are often difficult to heal, and may require surgery, especially in athletes.
Posterior ankle impingement & Os Trigonum Syndrome
Posterior ankle impingement is characterized by pain behind the ankle joint. Symptoms worsen during plantar flexion of the foot. Posterior impingement is differentiated from insertional Achilles tendinitis and retrocalcaneal bursitis, as these conditions are more closely associated with the attachment of the Achilles tendon to the heel bone.
Os trigonum syndrome is also a result of an overuse injury to the posterior tibia caused by repetitive plantar flexion forces.It is mainly seen in ballet dancers and football players. The extra bone is usually visible on plain x-rays.
Treatment is usually non-surgical, with rest, activity modification, anti-inflammatories and occasionally a cortisone injection. If there is mechanical impingement, or a large extra bone behind the ankle (os trigonum), treatment may involve removing the extra bone.
Achilles tendinopathy & rupture
Achilles tendonitis is a chronic condition characterized by pain and often swelling in the Achilles tendon. The symptoms are due to swelling and inflammation of the tissue surrounding the Achilles tendon. There are 2 main categories, insertional and non-insertional tendinopathy. Treatment is mostly conservative, with rest, ice therapy, anti-inflammatories, an exercise program, and PRP. Surgery is indicated in resistant cases.
Achilles tendon ruptures usually occur in athletic people in their 30s, 40s and 50s. The injury usually occurs after a sudden application of force resulting in the rupture (rupture) of the Achilles tendon.Achilles tendon rupture can be successfully treated conservatively or surgically. Recent studies suggest that nonsurgical and surgical treatment of Achilles tendon ruptures produce equivalent results.
Morton's neuroma
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition that affects the sole of the foot, usually the area between the second and third toes. The sensation most patients report is that they are stepping on a pebble.
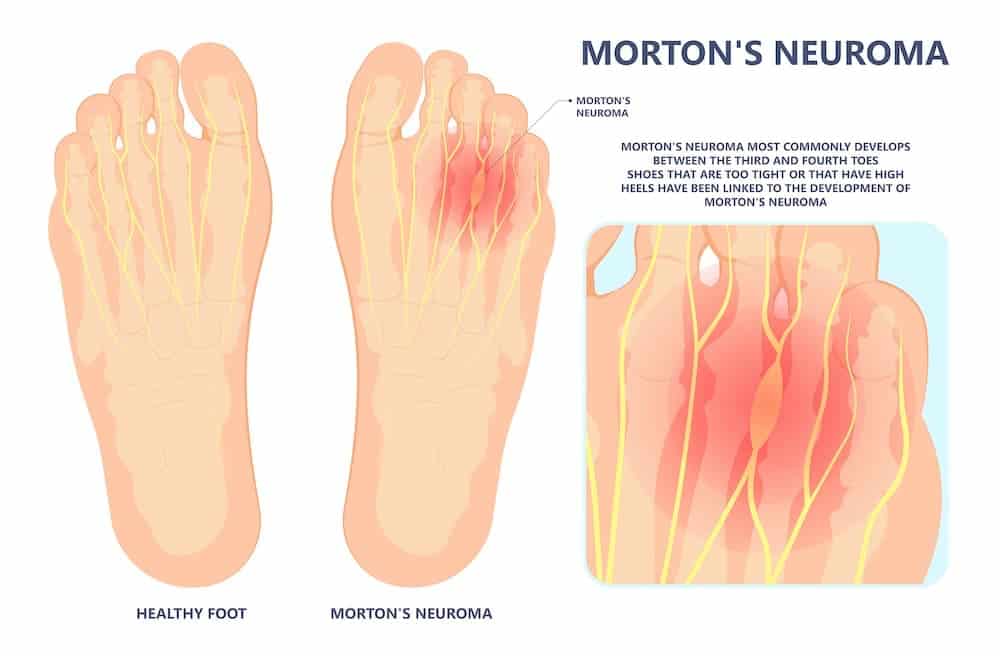
In Morton's neuroma, a thickening of the tissue develops around one of the nerves that innervate the toes. This can cause burning pain in the sole of the foot, and numbness or burning in the toes. Morton's neuroma appears to be the result of chronic irritation or repeated microtrauma to one of the nerves leading to the toes. If conservative treatment fails, a local injection of cortisone or anesthetic may be given. If this does not help, the next step is to surgically remove the neuroma.
Bunions
Hallux valgus, a condition also known as bunions, is one of the most common foot deformities. In this condition, the proximal phalanx of the big toe deviates outward resulting in the formation of an ossification (bone) on the medial side of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. A bunion is a relatively common condition. It occurs in about 23% of adults aged 18 to 65 and up to 36% of adults over 65.

The exact cause is not fully understood. It tends to happen more often in women and those who wear tight shoes or heels. Heredity also seems to play an important role. Based on x-rays of the feet, and depending on the angles formed between the bones, the condition is classified as mild, moderate and severe. Patients often report pain and difficulty walking. Initial treatment is conservative and aims to manage symptoms. In case of failure, surgical treatment is indicated. Usually, the surgery is done with a small incision, with an osteotomy of the first metatarsal (eg, Scarf, Chevron, Akin, etc.), accompanied by release of soft tissue and removal of the ossification.
Flatfeet
Flatfoot deformity is the condition in which there is a reduction in height or elimination of the foot arch. The incidence of the condition in the general population is high and can reach up to 30%.
Flatfoot is referred to as flexible, when the arch is absent during bearing but reappears when the foot is not bearing or standing on tiptoes. This form is benign – it causes no problems, or causes pain only with vigorous activity. Otherwise, we are talking about rigid flatfoot, which often coexists with serious diseases and causes pain during daily activities.
One of the most common causes of flat feet in adults is a dysfunction or insufficiency of the tibialis posterior tendon.
In most patients, a flexible flatfoot is asymptomatic and does not cause pain. In these cases, there is usually no cause for concern. Treatment of flat feet is indicated if pain is caused in the feet or soles, or if the condition affects the knees or lower back. Treatment may include special foot exercises, special arch support insoles, or splints.
In some cases, surgery can provide permanent relief. Common surgical procedures include flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer and calcaneal osteotomy for tibialis posterior insufficiency, or triple arthrodesis in advanced flat feet.
Arthritis
The most common forms of foot arthritis are:
- Ankle arthritis: primary or post-traumatic.
- Subtalar arthritis: often post-traumatic.
- Hallux rigidus: arthritis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint.
The treatment here can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the area, severity, stage, etc.

Toe deformities (hammertoe – claw toe – mallet toe)
Hammer toe is a common deformity of the toes. In hammertoes, the last phalanx of a toe is permanently bent toward the ground. As a result, a painful callus appears, both on the dorsal surface from the pressure of the shoe, and on the tip of the toe, from the pressure of the ground when walking. When the deformity is severe, the base of the toe bends and lifts away from the ground.Then, the angulation of the toe can become particularly acute, a condition called claw toe. Another similar condition is mallet toe. When conservative treatment fails, especially in painful and severe deformities, surgical treatment is required.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What's a bunion?
It is the deformity of the big toe, and it causes aesthetic and functional problems. It is painful and afflicts a large part of the female population. The big toe takes on an inclination towards the rest, while the first metatarsal projects in the opposite direction.
What's Os trigonum syndrome?
Os trigonum syndrome is also a result of an overuse injury to the posterior tibia caused by repetitive plantar flexion forces.It is mainly seen in ballet dancers and football players.
Find us
Book an appointment with us today

